What is SEO?
<< SEO Basics
SEO vs. SEM >>
<< SEO Basics
SEO vs. SEM >>
What is SEO?
SEO means Search Engine Optimization and is the practice of getting traffic from a search engine’s organic rankings.
And to achieve that some of the activities you perform are – keyword research, content creation, link building, and technical analysis.
In other words, SEO is all about growing ranking in the search engine’s non-paid section on SERP (Search Engine Results Page)– obviously, to increase organic traffic.
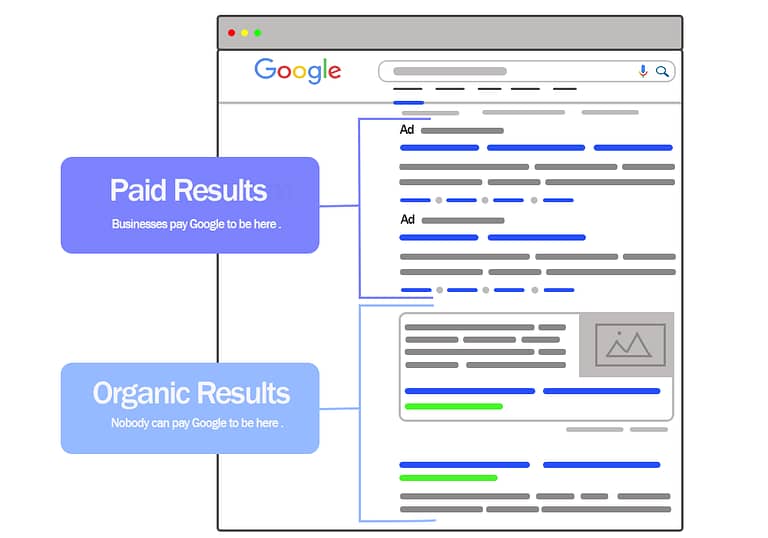
There are usually two types of results shown on a SERP:
Paid results
Organic results
A well SEO optimized webpage can get a huge traffic around a keyword consistently.
Why is SEO Important?
Have a look at mind-blowing SEO stats:

As you can see, 53% of the total website traffic that comes from organic search.
Organic search generates 10x more website traffic than organic social media and almost 4x more website traffic than paid marketing.
Let me take an example to explain you the value of traffic that gets generated through search engine optimization:
Suppose you’re running a online grocery store. According to Google Keyword Planner tool, 27,100 people search for “online grocery” every month.
And Google’s first result gets 20% of all clicks — that comes to (27,100*20%) 5,420 visitors per month if you rank #1.

Do you know how much those visitors worth?
On an average, advertisers spend 40 INR per click for that phrase. Hence, that means the web traffic of 5,420 visitors worth (5,420*40) 2,16,800 INR/month.

And you know that’s just for one search phrase. If your website is SEO friendly, then your site can rank of hundreds or thousands of other keywords.
The worth is even more if you are into industries like: legal, insurance, and real estate.
For example, an average advertisers pay over 70 INR for search phrase like “buy flat in gurgaon”.

Let me tell you some more amazing SEO stats:
- Google owns 91.54% of the search engine market share followed by Bing which has only 2.44% market share.
- 71% of clicks go to page one of the google results, out of which the first five organic results get 53% of the clicks. This clearly indicates that your position on the search engine results page is the decisive factor in the number of clicks you get on your site.
- Organic search drives 53% of traffic on Google.
- 95% of the search traffic leaves never bothers to visit the second page of Google search results.
- Over 1 billion people use Google every month.
- The #1 result on Google gets 33% of all clicks.
- It’s estimated that Google processes around 63,000 search queries every second. This roughly means 5.6 billion searches every day.
The topics we will cover in this complete SEO guide are:
How does a Search Engine Work?
It’s time for us to learn how exactly search engines work.
Most of the search engines including Google perform three major functions :
Crawling
Indexing
Providing Answers

Crawling
Crawling means when search engines like Google/Bing sends out bots/spiders to visit and download a page and extract links on the page in order to discover additional pages.
It is the very first step in the entire process.
Example:
Imagine you’re travelling to a new city – and want to see the entire city.
To do that, you’ll have to find the best possible way – may be a public bus that rides through the entire city.
Same happens with search engines. Since they want to crawl the entire web (that usually has a web page, but sometimes a PDF, JPG, or other file) – they also need a best possible way to travel to find the resources. And that best possible way for them is – Links.
The link structure of the web keeps all of the pages bind together.
Hence, crawlers travel through links to find new pages and what’s there on the page.
Indexing
Indexing means the search engine’s bots/spiders has understood the page that it has crawled – and considering it to be included in its database.
In other words, Indexing is the process of storing the newly discovered pages that Crawler has found.
If your website is indexed in Google’s database, it can appear in Google search results.
Providing Answers
Search engines are answer machines.
When a person performs an online search in Google, an algorithm gets to work and brings you that search engine considers the best result.

How does Google decide what’s the best result ?
Google doesn’t make its algorithm completely public. Though based on filed patents and statements from Google – we know how Google ranks web pages:

Relevancy
When you search for “leather shoes”, you don’t want to see results about cars.
That’s why most importantly Google looks at the web pages that are closely related to the search query.
However, Google doesn’t simply rank the web pages on the top that are most relevant – because there are thousands or millions of web pages that are relevant to each search query.
For example, search query “leather shoes” alone has 780 million results in Google:

Google considers two more ranking factors in addition to relevancy –
Authority
Authority is Google’s way to find if the content is accurate and authoritative.
How does Google determine the authority of a page?
Well, it just looks at the number of other links pointing towards the page. It’s also known as “backlinks”.
In other words, the more links a page has, the higher it will rank.
And Google’s ranking factor “authority” is what separates it from search engines like Yahoo, which came before it.
Usefulness
Imagine you are a person who does not belong to a science background and has searched for “air purifying plants” on Google. Among many other sites, NASA is one such site that ranks.
With real data and personalized research, it is obvious that you’ll find high-quality and authentic data on their page.
But here’s the twist! As you begin reading their blog on air-purifying plants, you find yourself constantly interrupted by heavy words that are too scientific for you to understand. One can easily expect it when a blog is published by NASA.
Out of the desire to be updated by a trusted website, you might continue reading further. But as you continue, you’ll lose grip and find it confusing. Eventually, you’d leave the page and visit some other page.
What exactly happened here?
The content is undoubtedly relevant and authoritative. But if it’s not useful, Google won’t want it to show at the top position.
Even Google has said that there’s a difference between high-quality content and useful content.

On the other hand, you find a different content on the same topic. It’s well organized and written in a way that anyone can understand.
But not equally authoritative and trustworthy as previous one.
Still that page is going to rank higher based on “usefulness scale”.
How SEO Works
SEO is all about optimizing your website for the search engines where you want it to rank.
For example, search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, or YouTube.
Your ultimate job is to make sure that Google finds your web page as the best content for a person’s search.
I recently talked about how Google shows the best content on the top is based on three important factors:
Relevancy, Authority, and Usefulness.
However, that’s not all. In its Press Day on May 10th, 2006 – Google said there are more than 200 ranking signals.

But no one knows all those 200 ranking signals. Google has never listed them anywhere.
Hence, testing is the best way to learn things for yourself.
8 major Google ranking factors can be a good starting point.
Most people care about Google rankings. This is why we’re going to focus on optimizing your site for Google in this course.
Customer Persona and Keywords
Producing content is one of the major parts of SEO work.
Before knowing your customers and what words/phrases they use to search online – it’s almost impossible to publish content.
That’s the only way you can create websites that customers would love to hang around.
Interesting?
Let me show you how exactly you can do this:
Customer Persona
Customer persona is how your target customer looks like.

Example, if you have to sell some stuff – without knowing who’s your target customer. Your sales pitch won’t be effective.
In other words, it’s going to be very hard to sell without knowing if the customer is an adult person or just a teenager.
Hence, it’s extremely important for you to create customer persona before getting into the knitty-gritty of SEO.
Let me say it again, to succeed with SEO – you will need to create content around topics that your target customers are searching for. But if you don’t know the topics your customers are searching for, it will get impossible for you to create that.
To know what your target customers are searching online – start with creating a customer persona.
You can use a free tool that comes from Hubspot – Make My Persona tool.

This amazing free tool lets you create customer persona in a stepwise manner. At the end of the process, you’ll have a nice looking avatar that you can refer to time and again.
Find Keywords
Now that you have created customer persona, it’s the time to do keywords research.
Keyword research is the process of finding exact words or phrases that your targeted customers type into Google’s search box.
By and large, keywords are of two types:
Informational keywords: Keywords people use to find what you don’t sell.
For example, I sell SEO training. Hence, my main keyword is Seo training.
However, people interested in SEO training, should not be all the time searching to buy SEO training.
They also search for link building, content marketing tips etc. These keywords are informational keywords for my site.
Product keywords: Keywords people use to find what you sell.
Let’s continue the above example. As I mentioned SEO training is my main product. So keywords that fall into Product keywords category for my site could be like:
- SEO training
- SEO training course
- SEO training online
How about another example-
Let’s say you run an e-commerce store that sells leather bags. Your product keywords would be like:
- leather bags
- leather bags for men
- leather backpack
And Informational keywords would be like:
- How leather bags are made
- What leather is gucci bags
- What leather is best for bags
Organic Keyword Research Tips
First, use Google autocomplete.
You must have noticed when you type in Google – it gives you some suggestions:

These are the keywords people are typing in Google. And Google itself suggesting that.
Hence you should be adding them to your list of keywords.
Second, use Related Searches feature in Google:
After searching for your keyword idea in Google, scroll down to the bottom of the page.
It’ll show you Related Searches to your keyword:

I recommend you consider them adding to your keyword list.
Third, use free tool AnswerThePublic to find informational keywords that people are typing into search engine:

For example: If you run a blog about Yoga. Then you will type Yoga into the search box at AnswerThePublic.
It will return you question people are asking around the topic Yoga:

For example, I found an amazing question ‘can yoga help back pain’ people ask around the topic –
can be a great topic for a blog.

Next, use keyword research tools:
- Google Keyword Planner
- SEMrush
- Moz Keyword Explorer
- Ahrefs
- Keywordtool.io
- Seed Keywords
The best free tool out of above is Google Keyword Planner.

Though the tool is designed for paid Google campaigns. But it can still help you find SEO keywords.
Head over to Google Keyword Planner, type your informational or product keyword.

The keyword planner tool will show you data for the exact phrase and a huge list of related keywords.

The data under average monthly searches tell you – how many times the phrase gets searched on Google.
The higher the volume is, the higher the search is.
Finally, if your website is completely new – you want to focus on long tail keywords.
Because long tail keywords are less competitive and can help rank your new site faster.
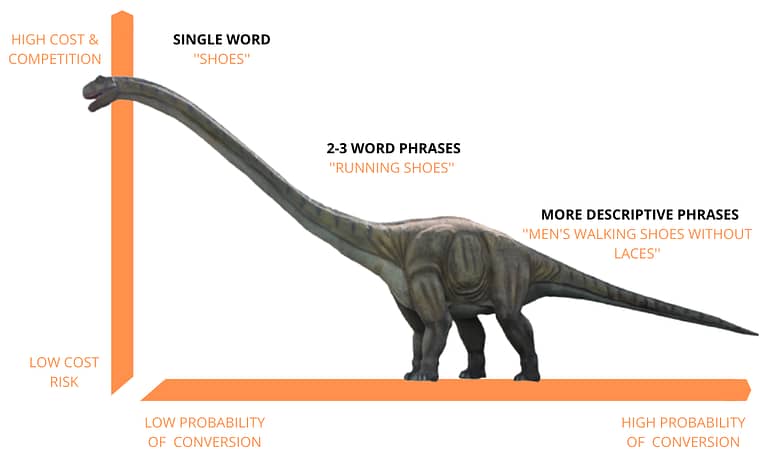
Once your site starts hitting some traffic – you gradually can start moving towards short keywords that are more competitive than long tails.
For example, my site is not very old. So I mostly publish content on long tail keywords like:
White hat SEO training
My site ranks #1 in Google for the keyword.

SEO Optimized Content
Content is the foundation of SEO.
A general thumb rule, the better content your site has, the more higher it’ll rank.
With that- let’s get into more details of SEO friendly content.
You mostly write content for three types of pages on a site:
Product pages
Service pages
Blog posts
Product pages
SEO content rules stay the same irrespective of the type of a page.
However, that doesn’t mean you’ll write content for your page like a blog post.
The purpose of product pages is to convert visitors into leads.
For example: look at the product page from Airifier.

This page is not a blog post or article. But it has a great quality picture with some highlights and features of the product.

So someone looking for a peace lily plant will get a lot of value from this page even though the main goal of the page is to get you to buy the product.
In a nutshell, make your product pages as helpful as possible. But don’t forget the number 1 goal of a product page is conversion.
Service pages
For example, look at this amazing homepage from Mailchimp.



Again, the page has no content like a blog post or article. But still the page provides a great visual insights of features Mailchimp offers.
Blog posts
When we say blogs- that means super useful content.
A survey of 1067 bloggers shows the bloggers who publish lengthy blogs get better results.
Do lengthy blogs provide useful content?
The truth is:
When it comes down to Google rankings, and social shares – long form of content tends to outperform short blog posts.

The same survey also tells bloggers who publish more frequently get better results.

With that– let me show you some examples of high quality content blog posts.
Roundups
Interviews and roundups are the most effective but least popular formats.
Here’s an example of an awesome roundup post from Nichehacks.

This roundup article alone is bringing a huge organic traffic.

List posts
List posts are the posts where you create a list of tips, techniques, items, ingredients, reasons etc.
The biggest benefit of list posts for the users – instead of reading 5 different blogs, they’re getting a blog with everything they need to on a single page.
For example, I published a list post on digital marketing my blog sometime back:

And it’s bringing some hundreds of visitors per month.

In-depth guides
In-depth guides are complete coverage of a particular topic from every possible angle.
For example, if someone wants to know in and out about a topic. List post guide won’t be of much help.
That’s where complete guides come into picture.
How about an example post:
I published a complete guide on “zero-click search” that covers highly actionable tips as well as Google’s take on this and why it can’t be ignored.
This post can be extremely useful for people, who want to know everything about the topic.
This post attracts hundreds of visitors each month.

Step-wise guides
Step-wise guides are a complete list of a process starting from point zero till the last step.
For example, if someone has just started to learn about SEO and wants to learn about keyword research from scratch.
The most useful content for the person is: simple steps to do keyword research.
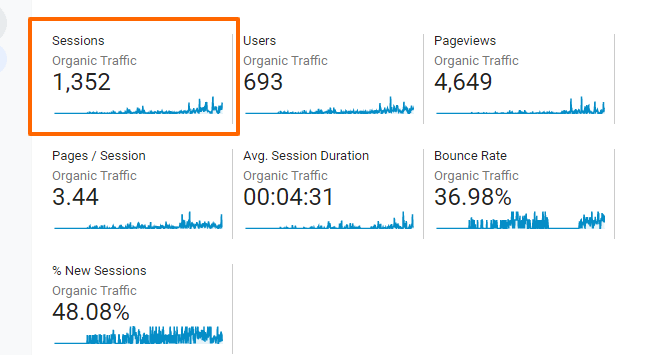
I also produced a step-wise guide having highly actionable tips on keyword research.

And also let me show it’s performance-
Not only it’s bringing visitors but they’re spending good time reading it as well.

Visual Content
Visual content gets your message across faster.
Also a recent study has found out Infographics are one of the most effective content formats for bloggers.

One more thing – Infographics aren’t the only visual content format. There are videos, graphs, flowcharts and more.
You can have combinations of different kinds of visual content.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO makes sure that Google finds your web-pages to show them in the search results.
It involves tasks of – uploading relevant and useful content on the web-pages to show up in the search results for the queries you’re trying to rank for.
Google scans your web-page to understand what it is about.
For example, your page is about ‘dog food’ and if Google finds mentioning of ‘dog food’ several times – it will think the page must be about ‘dog food’.
‘Dog food’ is your target keyword.

Let’s stop guessing and start with how to optimize your site on-page SEO.
If you’re a WordPress user–
I highly recommend using the RankMath plugin.
Heads-up: RankMath isn’t a magic tool but it can provide a great help for on-page SEO.

RankMath has a ton of other features to help you optimize your site for on-page SEO.

Use your target keyword in the Title Tag
Why?
Google uses your page title to understand what the page is about.

There’s a slight correlation between the usage of keywords in the title tag and rankings.
In a nutshell, title is one of the most important parts of your page.

For example, I published a blog with a target keyword ‘keyword research’.
So I made sure that I’m using my exact target keyword in the title tag.

Optimize Meta Description for higher clicks
Write a unique meta description solely for the audience.
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact the search results.
They are a summary of what a particular page is about.
Google has confirmed they don’t use a meta description to decide ranking.

However, a well written meta description can increase number of clicks and that can indirectly boost your SEO.
For example, have a look at a meta description for my article: keyword research.

If you have observed the meta description nicely– you must have noticed the target keyword appears in bold.
Right?
So when a user searches for some keyword and if that keyword is present in the meta description, Google will bold it.
And that gives the users even more reasons to click.
Hence, make sure you also use your target keyword in the meta description.
H1 Tag
H1 is usually used to mark up a web page title.
Don’t get confused with meta title.
Some CMS naturally place page title as H1 – but you can always change it.
However, the process varies from CMS to CMS.

Google’s John Mueller said H1 tags help Google understand the structure of the web page.
I’d say– more than Google it helps users understand the structure of the page.
The H1 is the most important heading tag on a page, then comes H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6.
Imagine a page using them not in the proper order– that can be hard to understand the hierarchy of the content.
How to write H1 tag?
Google recommends match the title of your page (Meta title) to the title of your article (H1).
However, there’s no harm if they both are slightly different from each other.
Ultimately, they both should be telling the same thing irrespective of having the exact words.
They shouldn’t be dramatically different from each other.
For example, suppose your page meta title tells about ‘how to lose weight with green tea’
and H1 tag on the same page tells about ‘lose weight with yoga’.
That’s bad, right?
Note: You can use more than one H1 tags on the same web page if it makes sense.
Finally, let me show you how to quickly check H1 tags on a web page.
Download a Google extension: Ahrefs SEO Toolbar.
Click on ‘Show on page SEO data’,
a window will pop up– scroll down to see the H1 tag used on the page.

Image alt text
Image alt text is a text explanation of what the image is about.
It’s also known as alt descriptions and alt tags.
Why is it important?
Image alt text mainly has three functions:
A. It helps screen-reading tools describe the images to visually impaired people.
B. It provides a better image context to search engines; hence, helping them to index images properly.
C. When an image fails to load on a web page, it shows up.

How to write image alt text?
Two important things to keep in mind:
First, the main goal of writing image alt text is that it should help visually impaired users understand the image well.
Hence, make sure you describe your image as if even when you close your eyes and someone reads the alt text to you, you can visualize a reasonably accurate version of it.
Second, it provides you another opportunity to include your target keyword to provide signals to search engine that your page is highly relevant to a specific search query.
But don’t forget the main purpose of the image alt text, and include your target keyword only if it makes sense to do so.
How about an example:

Best alt text for the image above:
“a woman having black backpack with covered head with a scarf looking at snow clad mountains”
Note: The most screen-reading tools cut off the image alt text around 125 characters. Make sure you don’t cross the limit.
Use keywords in the content
Next thing comes to mentioning of keywords in the content.
Start with mentioning your target keyword once in the first paragraph.
For example, I published an article for the target keyword ‘facebook organic reach‘.
I am using the ‘target keyword in the beginning of the article:

And I used the targeted keyword on the entire page is just 3 times.
And it’s a 2500 words article.
Keyword frequency doesn’t matter.
As you can see, it’s bringing hundreds of visitors on a weekly basis from Google, and not only that readers spend over 6 minutes reading this article.
So use your targeted keyword naturally, don’t try to include it intentionally.
Note: Google can understand your content even without having exact keywords in the content. But if you write naturally, you’ll end up mentioning the target keyword a few times. Don’t go overboard. Write for the users not for Google.

Use Synonyms and Closely-related words
Google isn’t around keywords, it’s around the topic.
Hence, you need to make sure your topic has rich content without abusing the targeted keyword.
One way of doing that–
Include words that are synonyms and closely related to your main keyword.
To do that–
Head over to Google and scroll down to ‘Related searches’ feature.
Google will show you the related phrases to your targeted keyword people are searching for.
Similarly you can find them on Bing.

Example–
In my blog, that has target keyword: keyword research.
I included one of the related keywords:
keyword research tools

Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to making your site technically sound to increase the rankings of it’s pages in the search engines.
A website is technically sound when it’s pages are:
crawled and indexed as desired and it also includes website loading speed, architecture, mobile friendliness and more.
Technical SEO is a huge topic. But you don’t have to worry about if your site is on a platform like WordPress.
With that, let’s jumpstart with it.
Search Console
Search Console is an amazing and free tool from Google.
It helps you to keep an eye on indexing status and visibility of your site in Google.
To use it–
First, verify your site with Search Console.
Second, upload an XML sitemap, of course once the site is verified.
It will open up a whole new world for your site.
You will be able to see–
- How many visitors are coming to your site?
- What do they search in Google to find your site?
- What are the pages getting higher number of visitors?
and much more.

Search console also reports issues related to crawling and indexing for your site.

URL Structure and Canonicalization
Create short, easy to read and easy to understand URLs.
How about an example:
https://www.seomarketing.com/blog/seo-ppc
Here the URL clearly tells you that this is SEO marketing blog page about seo and ppc.
Now look at this URL-
https://seomarketing.com/b2b-marketing-blog/blog-topics/marekting/pay-per-click-and-search-engine-optimisation
Does this URL help you easily understand what it’s about?
No, right!
Things to keep in mind when creating a URL:
- If you have a category URL like example.com/yoga, then make sure yoga related pages fall under same category page: example.com/yoga/boat-pose
- If you don’t have categories. Then keep it simple: example.com/page-name
- Use your main keyword. But don’t abuse the opportunity. Make sure it only comes once like: example.com/main-keyword
- Keep it short. Short URLs are easy to read and understand. Hence, they’re more user friendly. Search engines like them too
A study says, shorter URLs rank better in search engines.

Now, do you want to change your old URLs?
Let me explain with an example:
I recently updated an old blog and I didn’t like the URL so I changed it too.
It took Google a long time to index the new URL and till date it’s not getting the traffic the old URL used to get.

My suggestion: leave the old URL as it even if it’s imperfect.
But if you have decided to change it then make sure you do 301 redirect.
301 redirect will send all visitors from the old URL to the new URL.
This way you can minimize the traffic damage.
And if new URLs has created a lot of pages with similar content, then use canonical tag on the duplicate pages.

Site Structure
Site structure refers to how you connect individual pages on your website for a flawless user experience.
And it also helps Google better crawl your website.
You don’t realize site structure is a problem with new websites with a few pages.
However, a big website with no site structure can be a huge problem.

Two important things to keep in mind for a well-structured site:
First, create an organized website also known as ‘hierarchical structure’.
Hierarchy helps your site be organized into categories.
For example, if you’re running a men’s clothing e-commerce. Then you can organize your product pages into two categories: Formals and Casuals.
Second, create internal linking. With internal linking– you’re telling Google what are the most important pages on your site.
Note: Don’t abuse keywords in your Anchor text when creating internal linking. But also don’t use irrelevant Anchor text. For example: click here, link, etc.
Website Speed
No one likes a slow-loading site. No users, not even Google.
A famous Amazon study on loading speed says every 100ms delay in page load time costs 1% in revenue.
The good thing is: you don’t need to guess about your site loading speed.
There’s a free webpage speed test tool from Google: PageSpeed Insights

This tool gives you site a score on a scale of 0-100.
Note: PageSpeed Insights gives you separate scores for Desktop as well as Mobile. Mobile score is more important since Google is mobile first indexing. That means Google priorities the mobile version of web pages for indexing and ranking.

This tool doesn’t stop here.
It also gives a complete list of action items to improve the page speed.

If you’re using a CMS platform like WordPress–you can perform most of the recommendations using some plugins.
Mobile Friendliness
Majority of the users to a site comes from a mobile device.
That’s also a reason why Google has fully moved to Mobile first indexing.
Google prefers mobile version of your pages over the desktop versions.
To test your site for it’s mobile friendliness– head over to a free tool from Google:

No Interstitials on Mobile
Interstitials can frustrate users.
So pages with interstitials provide bad user experience.
Content on the page should be immediately available without any obscurity.
Hence make sure you don’t use any popup, and standalone interstitials.
Here are the interstitials examples that could make content less accessible:

To check mobile-friendly signals for your site:
Head over to Search Console–Mobile Usability report:

Set-up HTTPS
HTTPS makes your site connection secure.
But does it improve Google ranking?
Moz has a study published over it–that says using HTTPS has a very low boost on your Google ranking.
Google prefers secured sites over non-secured sites.
According to mozcast, 98.5% of Google results are HTTPS results.
In-fact, Google shows non-https sites as not secured.

No users would like to visit URLs that are not secured.
Hence, from the user experience standpoint–it’s crucial that you should move your site to HTTPS.
But once your site is completely moved to HTTPS–make sure that all your non-https pages are redirecting to https pages.
Google Analytics
How do you know if your SEO efforts are bringing desired results.?
Use Google Analytics to track your SEO performance.
Here’s how GA can help you:
- You can track organic traffic dips and spikes;
- You can identify pages that bring the most traffic to your site;
- You can easily find out bounce rate and time spent on pages, further this can help you better organize your content;
- You can create specific Goals to see if traffic is bringing quality visitors to your site;
- You can set up conversion tracking to see if the traffic that’s coming through SEO is converting into leads or sales.

Link Building
Link building is the process of getting mentions about your site on another site.
It’s also known as Off-page SEO.
Links are one of the most important ranking signals in Google.
In-fact, Google’s Andrey Lipattsev reveals links are one of the top ranking factors.
Also Perficient’s study has found a strong correlation between Google’s ranking and links.

Hence, links are super important when it comes to Google ranking.
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of how to create backlinks– let me show you link-building basics to consider:
Link Authority–
Not all links are equal, links coming from trusted and authority sites will pass more PageRank than a link from a low authority brand new website.

How to measure the authority of a website?
Check for these two factors:
Domain Authority:
Domain Authority (DA) is a search engine ranking score developed by Moz that predicts how likely a website is to rank in search engine result pages (SERPs).
Domain authority means the authority of the entire site. Even if a page doesn’t have a good amount of links–the page will still have some authority.
Page Authority:
Page authority refers to the authority of that single page only.
To check DA and PA, check the free Moz tool: Link Explorer

With that- you should focus on creating backlinks from high authority sites.
And it’s not easy to do.
Get Links from Relevant Websites
When it comes to links, a site’s authority matters.
But site relevance also matters.
Getting a link from another site is like getting a vote in your favour.
And that vote will pass more SEO juice if it comes from a relevant site.
Links from a relevant site will also confirm Google that it’s a genuine link.

For example:
Let’s suppose I get two links one from some tattoo parlour website and the second one from some digital marketing consultant blogs.
Links are votes.
Which is the vote out of the above two will you trust more?
Quite an obvious answer would be the second vote.
Right?
Google thinks the same.
Note: It’s ok to get links from sites that are not relevant to your site. But if those links are the majority of the links you’ve got for your site– can create a problem.
And relevant links don’t necessarily mean they should come from the sites on the exact topic.
For example:
If I get a link from a website developer website, that link is related. Topics are different, but the industry is the same.
Get Contextual Links
Contextual links are those links that are placed in the body of a web page’s content.
Links in the main content are more likely to be clicked and that makes them of high quality.
Links that are placed in the areas such as a footer or sidebar area don’t pass that much SEO value.

Focus on Links from Unique Referring Domains
It’s always better to have 100 links from 100 domains than 1000 links from 100 domains.
A study confirms a percentage of links that come from unique referring root domains pass more PageRank.

How to get other sites link to you?
Before starting with the techniques–let’s understand Black Hat vs. Grey Hat vs. White Hat link building:
When you will start with creating backlinks–you will come across things like Black Hat/Grey Hat link-building strategies.
Black Hat as well as Grey Hat are link-building techniques that are against Google webmaster guidelines.
In real world, they don’t work rather may get you some Google penalty.
How to judge if specific link is not legit:
Link-schemes list:
Google has a link-schemes list that explains shady link-building techniques.
Paid-links:
Have you paid to get a link? Exchanging money or goods for links is against Google guidelines.
On the other hand, if you have “Earned” a link–means if some other website has linked to you because they think it’s worth to link to you and will increase their content quality.
Then you have no problem with the link.
With that, let me show you some amazing white hat link-building techniques:
Email Outreach
Email outreach refers to the process where you reach out to people in your niche and introduce them to your content.
That content might be your in-depth blog, a product or service page on your site, your brand page, etc. All in all, you need to have something worthy of link.
For example, many people link to Ad School Master because they find our SEO tips are worthy enough to mention on their sites.

This is good enough information that tells you to create an email outreach strategy. Because this blog on our site helps people specifically on how to deal with zero-click searches.
So why not reach out to more people who need the same solution.
If they find it useful, they also can link to the blog.
How do you start with email outreach?
Just follow 2 simple steps:
Create linkable assets
“Linkable Asset” is something people will love to link to.
For example, if you publish the top 20 yoga benefits, people are not going to link to them because they’re already hundreds of such articles on the internet.
So, create something that’s specifically created to get links.
Some examples of linkable assets are:
- Case studies
- Original research and studies
- Free Tools
- Industry trends and statistics
- List posts
- Infographics
Reach out to people
Once your linkable asset is ready, make sure you promote it.
To start with that–
First, send emails to people who’ve mentioned your target keyword in their articles.
For example, to find out articles that use the phrase “advanced yoga tips” in the body text.
Search using a Google search operator:

This will only return results where advanced, yoga, and tips are all mentioned within the body of the text.
Next, to find the email ids for the authors who have published the articles–use email finder tools.
Let me show you how to do that using free tool hunter.io

Finally, inform them about your ultimate piece of content on the same topic.
Additionally, share your content on social media platforms like – Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, etc.
It can help you grab some more eye-balls. And who knows you may get some links as well.
Guest posting
Guest posting means writing an article for some other website, in-return you link to yourself from that article.
It’s that simple and also one of the popular methods to get some early links.
At the same time, it’s extremely controversial too.
Because many people do black-hat link-building in the name of guest-post.
Things to keep in mind while doing guest-posting:
- Do guest-posting within your niche. Publishing lots of guest posts on unrelated websites might get you in trouble.
- Avoid using keywords in the anchor text when linking out to your article. Instead, use your brand name. (for example: Ad School Master)
- Don’t create a lot of links using guest-posting. That can make Google suspicious.
How to start with guest-posting?
First step is to find the websites that offer guest-post.
For that:
Use Google search operator–
topic + intitle:”write for us”
This will show you “write for us” pages, from the sites that allow guest bloggers.

Reach out to them, pitch your topics, and get your first guest post published.
Note: Don’t forget to check site authority before publishing an article for it.
Broken link building
This is probably the easiest way to get a link.
You just have to do three simple steps to get such link:
- Find a relevant broken link on a website;
- Check in the Wayback Machine tool. And create something similar to be broken resource;
- Ask anyone linking to the dead resource instead link to your working resource.
For example, I work in SEO niche.
Let’s find a broken link together.
Install Use My Links
It’s a free Google chrome extension.
Once it’s installed–you’ll see a little icon in the top right corner of Chrome.

It will report links that are broken on the page.
Note: First, find pages that have lots of links. Because the more links a page has, the more likely one of them is going to be broken.
Next thing, check that broken page in Wayback Machine.

And it’ll show you, how that page looked like when it was a working page:

By now–
You have the broken link as well as the content it had when it was a working page.
Next thing, create similar content.
Once you have the content ready, reach out to sites that are linking out to the broken link.
Inform them about it and offer them your working link that has the similar content as the dead page had.
Skyscraper Technique
In 2015, Brian Dean revealed a link-building strategy he used. He called it the Skyscraper Technique.
In this link-building technique, you improve existing popular content in your niche and replicate the backlinks.
It takes three steps to implement the Skyscraper technique;
- Find a relevant piece of content with lots of backlinks;
- Create something way better;
- Ask those linking to the original content to link to your better content instead.
To know more: here’s the detailed study that will walk you through the steps.
Search Intent
Search intent (also known as user intent, or audience intent) is the term that’s used to describe the purpose of an online search.
It’s the main reason why someone performs a search.
There are four types of search intent:
- Informational intent;
- Navigational intent;
- Transactional intent;
- Commercial investigation.

If you don’t understand the user intent; a high chance that you won’t do good as SEO.
Let’s take an example to get a hang of it:
When you want to go out to have Indian food, you’ll search for “indian restaurant gurgaon”.
That’s a transactional query.
But when you want to cook Indian tandoori chicken at home, you’ll search for “how to cook indian tandoori chicken.”
And that’s an informational query.
Hence, to get a higher Google ranking– make sure your content is in sync with search intent.
How about another example:
Let’s say you’ve got these keywords on your list:
- green tea maker
- green tea vs white tea
- single cup green tea maker
- how to make green tea for weight loss
If you run an online store with a blog, you need to understand which keywords to target with blog posts vs. product pages.
For a keyword mentioned above, you wouldn’t create a product page “how to make green tea for weight loss”,
because that doesn’t make sense.

And also people who are searching for this keyword are not looking for buying tea equipment.
But for a keyword like “green tea maker,” you should create a blog post about the best green tea makers or an e-commerce category page showing all the green tea makers you sell.
I’d recommend you should double-check Google search results for your keywords to understand the search intent better.
Because Google’s search algorithm understands search intent better than anyone.

If you want to stand the best chance of ranking, you should create the same type of content as you already see ranking on the first page.
Or
If you’re confident that you can get searchers’ attention with a different content type, or format, give it a shot.
User signals
How does Google know if your content is a great fit for user intent?
To do that–Google’s algorithm closely observes ‘behavioral signals’ to figure out whether users were satisfied with the search engine’s results.
Some websites claim Google uses CTR as a direct ranking signal.
On the contrary, you will also come across websites that claim pogo-sticking is the preferred ranking signal.
Though there is not enough evidence that supports such claims.
Google has confirmed CTR is used alongside other engagement signals. And John Mueller has suggested Pogo-sticking isn’t something site owners need to worry about.
With that, I’d recommend you should pay close attention to important metrics together:
- Dwell time
- CTR
- Bounce rate
- Pogo-sticking
How to optimize for user signals
First of all, make sure your content aligns with search intent.
If it’s not, Google will start downranking your webpage.
Once it’s fixed, here are some other things you can do:
- Create amazing content. Don’t focus on producing regular content. Amazing content has– compelling intro, benefits for users, then followed by tips with lots of visuals (images, and graphics), because high-quality content increases time spent on the page, lowers the bounce rate, and provides useful content.
- Don’t forget people love reading fresh content. Hence, keep your content fresh. Don’t just change the date every year. For example, if you created a list of tools, then you can update the screenshots and pricing.
- Make sure your website is loading fast and mobile-friendly. A majority of users on a website come from mobile. According to Pingdom, Fast-loading websites have a low bounce rate.
- Create strong internal linking. Internal linking helps users, as well as Google, find your pages better. That way, people can learn about topics you cover in an article without bouncing back to SERP. It also passes some authority to a newly created page.
SEO Trends
Once you find yourself comfortable with fundamentals of SEO–you can use emerging SEO trends to advance your content.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are additional data displayed with normal Google search results.
Does it improve search ranking?
According to Google, it’s not a direct ranking factor.
But look at the two Google results:

The result at the top is a normal snippet.
The second result that’s showing lots of additional information like– star ratings, number of reviews, time to cook, and a picture of chicken curry is known as the Rich-snippet result.
They look much nicer than normal snippets.
And the users will instantly get more information, just by looking at them.
This is something great for the visibility of your site, can also increase the number of clicks on your result.
When people will prefer your page above other ones, Google will notice that your page is a better result for that specific search and that will certainly improve your rankings in the long run.
To learn more– read this complete guide on Rich Snippets results.
E-A-T
E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
With E-A-T, Google wants to be 100% sure that the content in search results is trustworthy.
E-A-T is important for all queries but for some, it’s even more important.
For example, if you’re just searching for pictures for cute dogs, then E-A-T probably doesn’t matter much.
But if you’re searching for the correct treatment to cure your migraine, then E-A-T is undoubtedly important.
If Google were to ascertain that the content on this website is written by some clueless writer, published on an untrustworthy site, and lacks authority–then a high chance that your content is misleading.
Because the nature of information in this content is extremely sensitive and can be life-threatening.
How about another example?
E-A-T is also important for queries related to your finance.
Let’s suppose you’re suffering from a bad credit score.
You head over to Google and search a query “how to improve credit score”.
Here a piece of advice from some random freelance writer is unauthoritative and can’t be trusted.
Google refers to this kind of topic as YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics.
My suggestion–If your site is built around YMYL topics, then make sure you publish high-quality content that’s written by experts.
In Google’s search quality guidelines, Google hints out that even links help them determine E-A-T.

Voice Search SEO
Voice search is on the rise and people are not only doing voice search at smart speakers (Alexa, Google Home, etc.) but at mobile phones too.
41% of adults use voice search everyday.
And this is why you can’t ignore: Voice Search SEO.
People asking questions at smart speakers may not visit your page,
same people when they ask questions at mobile phones but this time with the intent of visiting a page.
According to Google, 20% of mobile searches are voice searches.
And it’s increasing.

Bottom line?
Voice search trend is significant in the world of SEO and Digital Marketing.
To start optimizing for Voice Search SEO, read this amazing guide from Searchenginejournal.
Core Web Vitals
In June 2021, Google confirmed its long-awaited page experience update started rolling out.
Google said Core Web Vitals (CWV) is going to be part of the ranking system.
SEMrush studied the initial impact of CWV, and they spotted no surprising difference post this update.
You can check CWV reports for your site in Search Console:

RankBrain
Google announced RankBrain is its third most important ranking signal.
RankBrain is a machine learning algorithm (AI) that helps Google understand likely user intent of a search query.
It also helps Google process and understand search queries.
How to optimize for RankBrain?
If you pay close attention then you will understand–RankBrain has two major jobs to do:
- Understanding search queries (keywords) and
- Measuring how people interact with results (user satisfaction)
As it turns out, user-intent and user-satisfaction are two pillars of RankBrain.
Things you can do to impress RankBrain:
- Write compelling Meta Titles and Descriptions that will improve CTR;
- Create long-form useful content with amazing intros that will help improve dwell time;
- Create strong internal linking that will help you have better bounce rate and save users from pogosticking
- Use LSI keywords to provide RankBrain with more context that can help it understand your complete page. For example, if your target keyword is “cold brew coffee”, here LSI keywords can be temperature, cold water, ice, beans, grind, filter, etc.
YouTube Videos
YouTube is world’s 2nd largest search engine only after Google.

According to a study, YouTube videos are taking bigger part of search results. Especially–in the first fold.
If you want to learn more about YouTube– visit YouTube Creator Academy.

This means you can’t ignore YouTube instead having presence on YouTube is must for SEO.
If you want to learn more on that–visit YouTube Creator Academy.
SEO Automation
As you can see, people are starting to use AI and Machine learning much more.
There are tools that can produce meta tags, write content for you and much more.
I’m not saying they are 100% perfect. But we’re getting closer.
Use of python in SEO is increasing for automating Technical SEO and data analysis.
It’s also difficult to automate everything, but you can have tools that can do a lot of things for you that you would’ve done manually.
To learn more on this: read this interesting guide on SEO automation.
Previous
<< SEO Basics
Next
SEO vs. SEM >>

