SEO vs SEM
SEO vs. SEM
With millions of results available on each query, optimizing your website for the search engine’s result page is essential.
Google’s results can be categorized into organic search results and paid search results.
SEO means optimizing your website to rank for organic search results.
On the other hand, SEM is an umbrella term including organic results (SEO) and paid results (PPC).
Paid results are shown when you pay each time a user clicks on the ad for your website. These are also called PPC (Pay Per Click) ads.
Google highlights the paid results by ‘ad’ written on them.
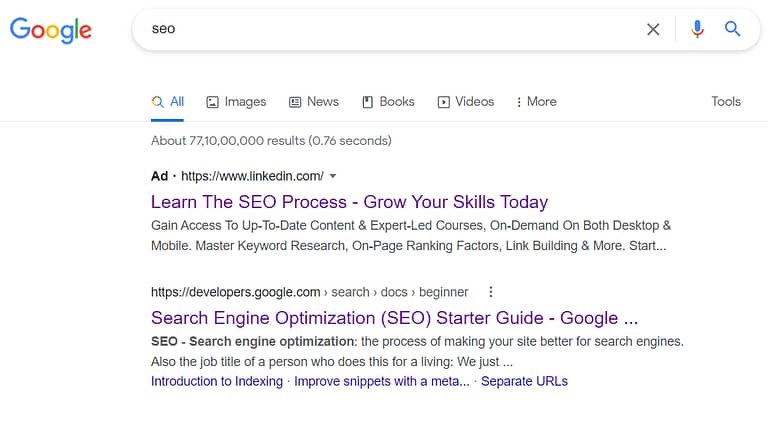
As shown, the first result uses PPC while the second one is SEO optimized.
Let us discuss them each:
What is SEO?
SEO means optimizing a web page to rank for organic search results.
A study by GroupM UK and Nielson shows that 94% of the total clicks on SERP go to organic results.
Google considers around 200 ranking factors in its algorithm before determining the order of ranking pages.
Unlike PPC, there is no payment for which you can get a higher ranking. So all you can rely on is hard work!
To optimize for SEO, you need to work on four primary areas. They are on-page SEO, off-page SEO, technical SEO, and user experience.
On-Page SEO:
On-page SEO refers to improving the visible factors directly related to your web page.
These include:
- Keywords
- Heading tag
- Title tag
- Meta description
- URL optimization
- Publishing long content
- Creating multimedia experience (quizzes, games, infographics, diagrams, etc.)
- Using relevant anchor text
- SEO optimized images (compressed, alt text)
Off-Page SEO:
It refers to improving SEO factors outside your website. It gives an idea to Google about how others perceive your website.
Off-page SEO revolves around link building.
Major off-page factors are:
- Internal linking your website.
- Diversity of websites linking to your site.
- Authority
- Relevancy
- Anchor text
- Number of domains linking.
Technical SEO:
It means optimizing for the technical factors of your website. No matter how good a website is, there’s no point if Google can’t find it! Crawling and indexing are the primary technical requirements of a website.
However, there goes a lot more into the technical aspects.
Main technical factors include:
- Compressed images (for fast loading)
- Clean codes on the website
- Sitemaps
- Making schema
- AMP versions for mobile
- URL canonicalization
User Experience:
Your website creates a particular impression on the mind of visitors. This experience depends on how efficient and effective your website is.
A good user experience for a site would be:
- Visiting your website
- Going through different pages
- CTA
You can consider the following factors for a better user experience:
- Clean pages (using white spaces, proper headlines, not flooding images, avoiding heavy paragraphs, not using multi-colors. etc.)
- Mobile-friendly pages
- No dead links
- Clear Call to Action (CTA).
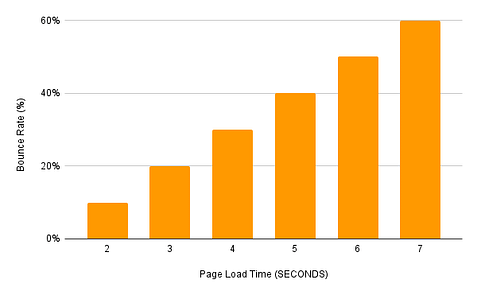
Bad user experience leads to an increase in Bounce Rate.
Bounce rate is the % of people leaving your website without taking any call to action, like, downloading a pdf file, making a purchase, clicking on links to social media, etc.
What is SEM?
Everything that we just discussed goes for SEM too. But as we discussed, it also includes PPC.
Here is an example:

If you click on the above result, it will cost them money.
In PPC ads, advertisers bid for placing their ads. Every time someone clicks on that ad, Google will charge some amount of money.
So, if your sales from the traffic generated through the ad are 1200 and you have paid 800 to Google, you still save 400.
So, every time a search query is made that has ads for it, Google looks for them and chooses the best ones to appear on the SERP.
There are many factors that Google considers including, bid amount, relevancy with the keyword, ad copies, etc.
Let us discuss various parts of PPC that you should focus on:
Google Ads Account:
To run Google Ads, you need first to have a Google Ads account. In case you have a Gmail id, enter it, create a password, and boom! You have an account.
Create Ads:
After creating your account, you need to do the setup.
Decide on a budget and choose the keywords. Use Google Keyword Planner to find a list of keywords for your campaign.
Choose the devices where you want your ad to run, set up your landing page, and finally write the ad copy.
Writing Ads:
You should be well-versed with the business you are creating ads for and do proper research.
It’s a small space where you have to write the ad, so be very selective and precise.
Use your keyword in the ad and at the top of the landing page, use a clear CTA in the ad copy, mention the features, benefits, reviews, etc.
Your CTR highly depends on the ad copy. A good ad copy will boost up your CTR, which will, in turn, increase your quality score.
Improving Quality Score:
Quality score is a score given by Google to your ad based on overall user experience (quality of landing page, ad copies, CTR, etc.) and relevance between the keyword and your ad.
The score ranges from 1- 10, 10 meaning the highest score and 1 being the lowest.
The higher the score, the less you pay for each click and vice versa.

Manage Ads:
Google ads have a three-layer structure, including accounts, campaigns, and ad groups.
An account has its email address, password, and billing information. The campaigns are made based on budgets and where the ad will appear. Ad groups are categorized based on similar keywords.
Bidding:
Every time someone clicks on your ad, you will be charged a certain amount of money.
Here, you choose specific keywords to bid on. When a user searches for that keyword, your ad will have a chance to show up.
An advertiser can decide the maximum amount they are willing to spend on each click, known as the bid amount.
The more the bid amount, the higher the placement of your ad.
Ad Rank:
Ad Rank is the overall value that decides your ad’s position.
The ad with the highest rank shows at the topmost of Google’s result page.
Here are the significant factors contributing to ad rank:
- Bid amount
- Ad quality and landing page
- Competition on the keyword
- User’s location, device, search context
When to go with SEO?
Limited Budget:
If you have just started or have little money in hand, go for SEO. Rather than exhausting your budget too soon, it will be better to use it wisely.
SEO allows you to have more significant results on smaller investments. You don’t need to bid on your keywords, unlike PPC.
Ranking for informational keywords:
Informational keywords have a high search volume, and if you manage to produce great content on such topics, SEO will do wonders for you.
Informational keywords also have more chances to have featured snippets.
As I am just starting, most of my blogs would be on such keywords.
Time Consuming:
There’s no doubt that SEO is time-consuming. So, it’s better not to have unrealistic expectations.
As per Ahrefs study, only 22% of the pages that rank in the top 10 are under a year old.
Doing good SEO means producing great content, acquiring high-quality links, improving site speed, and many more factors.
So, SEO requires a lot of hard work and patience.
Writing Skills:
As it’s said, “content is the king.” A significant part of SEO includes producing authentic and valuable content. With so many blogs getting indexed by Google every day, you can understand the competition.
But there’s always a scope for improvement! If you can come up with more researched and better content, you have chances to outrank them.
So, if you plan to do SEO, you must be good at writing content.
Building Links:
Link building is one of the most crucial and most challenging parts of doing SEO. But if you plan to stay for a long run, you can’t escape it.
SEO asks you to be good at various link-building strategies and finally doing email outreach.
When to go with PPC?
Good Budget:
Going for PPC is always a great idea if you have a good amount of money in hand. Your results hugely depend on how much you are willing to spend.
Quick Results:
While SEO is a long-term tactic, PPC is better for faster results.
If you are investing a good amount of money, you will get massive traffic in no time. Sometimes, it takes less than a day to get to the top of the results page.
But to get the best ROI, you have to do a lot of testing. That includes A/B testing, trying different keywords, bid amount, etc.
Knowledge of Google Ads Account:
You should know how ads work. It is essential to have some experience as you are dealing with money.
If you are a newbie, you might end up experimenting a lot. You can bid on keywords that are not highly relevant to your business and waste a lot of your budget.
So, you should have good knowledge about the ads account.
Optimization for Google Ads:
PPC needs to be constantly managed and optimized. Keep changing the targeting places and age group as per the results you get.
Optimize for the days and time during which your ad performs well.
Change your bidding strategies. You can also optimize your bid amount for specific devices like mobiles.
Try to change the ad copies, like headlines, do A/B testing with landing pages.
A/B Testing of Landing Page:
Landing pages are standalone pages created to focus on a specific goal or conversion. Unlike a homepage, a landing page is sheerly dedicated to achieving a particular result after the visitors’ land’ on the page.
A conversion can mean different things to different businesses like generating leads, downloading an e-book, or registering.
After a user clicks on a paid result, the next thing they see is a landing page.
While monitoring your ad, you may find that your conversion rate is less or people are not engaging.
It can be solved by doing A/B testing.
An A/B test is an experiment done by changing some page aspects to see which one works better.
This way, you can compare two different landing page models and see which one works better.
Good A/B testing is when you change one element and see how the slight change brings better results.
SEO vs. PPC: How much they cost?
Many people think that SEO is a free marketing tactic. You don’t have to pay for each click on your website, but it is NOT free.
You may not spend as explicitly for a PPC campaign, but there is nothing like free organic traffic.
Let us take an example of keyword research.
Though there are many free tools, they offer limited use and lack advanced features. Using them, you can only do narrow searches per day.
Though they are enough for light users, you will always need a paid version as you produce more content.
With a paid version of Semrush, I can get more features, more keyword requests per day, gather rank tracking data from multiple devices, and much more.

Your content should always be grammatically correct and match the tone of your business. To maintain this consistency, I use the paid version of Grammarly.
A plus point of the paid version is that you can check the plagiarism level. It becomes an integral part as you should always produce unique content.
I ran my check on recent content, and here’s what came:

I couldn’t have done it using the free version. Also, the paid version offers advanced sentence correction, like correcting passive sentences, rephrasing the ruling, offering better words, etc.
You would also need a tool for email outreach, especially during link building.
Superoffice.com says that the average open rate of emails is 21.3%.
With such a low rate, you should try reaching out to as many people as possible. But, a free tool only allows limited searches per day.
I used the unpaid version of Hunter.io for finding emails and faced the same problem. It only allowed me 25 searches/month.
I tried switching to other tools but got stuck in the same way.
I finally had to go for the paid version, and now I can smoothly find the email addresses without wasting any time.
But tools are just one part of SEO.
Apart from that, it would help if you also had a fantastic content writer to produce high-quality and original content.
But the content has to be interactive. It should have charts, graphs, infographics, etc.
For this, you will need a graphic designer. They should be comfortable with tools like Photoshop and Illustrator.
Then, I also used the paid version of the RankMath plugin. It is known as one of the best SEO plugins helping in advanced analytics, tracking your rank, and much more.
It also helped me achieve site links on SERP:

But even after putting in so much effort, you can never be sure with SEO.
On the other hand, PPC helps in achieving faster results. Once you are life with the ad, you can bid for your keyword and start receiving traffic.
As per WordLead, 65% of people click on ads when making a purchase. This suggests that the conversion rate by PPC is more than SEO.
It is especially beneficial to small businesses that want instant results.
But PPC has one big downside too!
Your paid campaign stops the moment you stop paying.
Unlike SEO, PPC is money-driven.
SEO takes longer to produce results, but they don’t fluctuate so fast. Once you have ranked on Google, you need to maintain that position without investing much money.
To sum it up, SEO can give you consistent results, whereas PPC can give you immediate results.
They both have their pros and cons and should be chosen as per the need of your business.
When to do both SEO and PPC?
There is nothing like driving traffic from both paid ads and organic results. But, it’s not as easy as it sounds.
Here are the prerequisites you must keep in mind:
Team:
Handling both SEO and PPC can not be a single person’s job. Moreover, one person cannot use expertise in all things.
It would help if you had an entire team to handle various tasks within each of these categories.
For example, you need an excellent writer to produce content, a graphic designer for designing images, a social media expert to handle social media accounts, a good copywriter for writing ad copies, a data analyst to analyze the data from ads, and SEO, etc.
Budget:
As you know, SEO is nowhere close to free. PPC, on the other hand, is money-driven.
So to leverage both forms of marketing, you need to have enough money to run PPC campaigns and continuously spend on SEO.
Skills:
If you are a startup, you should not experiment a lot. Go for SEO and PPC only when you have some experience and are confident enough to handle both the marketing tactics.
Previous
<< What is SEO?
Next

