Page Speed
<< Robots.txt
<< Robots.txt
Page Speed
The amount of time it takes for a web page to load fully on your screen is known as the Page Speed.
Page Speed is of the most important technical factors determined by various factors ranging from codes to the images.
Why Page Speed Matters?
Better User Experience:
When a user visits your website, they want to have instant access to all the information.
But if they find a blank screen, they will click ‘back’ and go to Google’s results page.
This is what we call as the Bounce rate. Here, user leaves the website without taking any call to action.
This will further lead to lower stay time on your website.
As per Neil Patel, 40% of people abandon a site that takes more than 3 seconds to load.
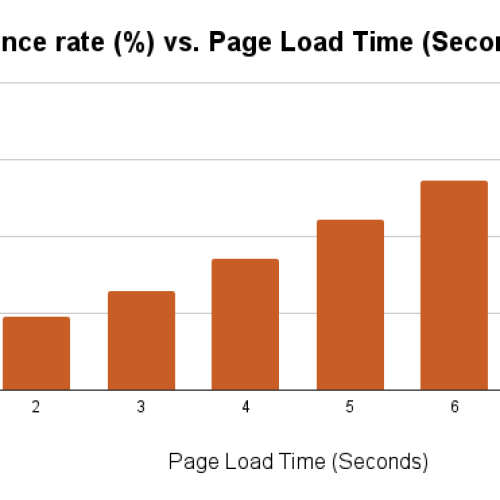
As clear from the graph, bounce rate goes down as the page speed increases.
Ranking Factor:


This clearly shows that the average load time of a site on the first page is not more than 2 seconds.
Increase In Conversion Rate:
Not only does a fast loading page keeps users but also helps in more conversions.

According to Neil Patel, 1 second delay in page response can lead to 7% reduction in conversion.
Walmart also found that increasing the page load time by 1 second can increase the conversion by 2%.
3 main factors to assess the Page Speed:
- Fully loaded page
- Time to first byte (TTFB)
- First meaningful text
Fully loaded page:
As it is clear from the name, it is the time taken for a page to load fully. This includes all the elements on the page like text, images, videos, animations, etc.
The page will only load fast when all its elements, in together, can load fast.
TTFB (Time to First Byte):
Sure, we can wait in long queues for a Sunday brunch or can wait for days before an online order arrives! But, when it comes to fetching results online, our patience shrinks majorly!
As the name defines, it is the time taken by the browser to receive the very first byte of information from the server. It’s usually in milliseconds.
In other terms, it’s the time taken by the server to receive the request and time in which it can deliver the data.
Google calls it ‘waiting’ in its language.
It happens in 3 steps:
Step 1: Making a request to server: when a person taps on your website, a http request is made by the web browser to the web server in order to fetch data. There can be a delay in this process due to many factors like, server being far away from the request location.
Step 2: Processing made by the server: this is when the server has received the request and processes it.
Step 3: Responding back: now, the data or the first byte is sent to the browser. However, if your network speed is slow, this process can get delayed.
Two clear disadvantages for a site that works poor with their TTFB are:
1. Number of visitors to your site will dramatically go down.
2. Search engines will not rank your page considering the fact that it works slow.
First meaningful text:
First meaningful text or first meaningful paint is the time taken by the primary content of your page to get loaded.
You must have noticed that sometimes a page appears blank before anything gets loaded on it.
As we discussed above in TTFB, users don’t have more than 1-2 seconds to wait for your page to load. With so much content out there, they are spoiled with choices.
However, there are a few smart ways to trick the users during the load time that will not make it look boring:
- You can create an illusion for the visitors during the loading time. You can use a small blurred image that will make them feel that the actual image is getting loaded and the page doesn’t appear to be blank.
- Blur-up is another tactic used to keep the visitors engaged. You can use thumbnails working as placeholders while the image is still getting loaded.
How to improve Site Speed
Page size / file size:
There can be many bulky files on your website including, high resolution images, videos, animations, graphics, etc. These can heavily hamper the speed of your website.
For example:
A quick image optimization is right here:
- Resize and compress your images
- Use JPG or PNG as per the requirement
Compression | Lossless | Lossy | |
PNG | Good | Yes | No |
GIF | Ok | Yes | Yes |
JPG | Good | Yes | Yes |
This suggests that JPGs are lossy compressions whereas PNGs are lossless compressions.
Many a times people use the Flash tool for making their site more interactive in nature. These are usually bulky files that take much longer to load than the regular content.
When a page is getting loaded, an HTTP request is made for every element that’s getting loaded. If there are too many requests for these elements, you need to cut down on them.
Make sure that your page is not too heavy as it will irritate the visitors and they will exit from your website.
Minify codes:
The major components of your site include images, HTML, JavaScript and CSS. In order to minify the codes on your website, you have to work on the latter three. The codes that your page has should be neat and clean with no unnecessary gaps in between.
The CSS, JavaScript and HTML also contain the requests that you make every time while loading the elements. By combining and reducing the size of these files, you can cause faster loading of these elements.
Hence, your web page gets loaded faster by working on your codes. Try replacing extra code lines with smaller ones and keeping it light.
Cache plugin is used to achieve the same.
Hosting service:
If you have a new website, you are likely to buy a cheap hosting. In the beginning, the drawbacks of buying a cheap hosting may not be much visible, but as you add more content on it and the number of visitors on your site increases, this will start causing problems.
The three main types of hosting include:
Shared Hosting: This is the cheapest option in hosting services. Your website can load slow due to other websites present on the same server. Generally, people with new websites prefer to go with it.
As the traffic and content on the site increases, Shared Hosting can become a major reason for decreased site speed.
- Dedicated Server: Here, only you have the access to the whole hardware of the server. It allows you to have maximum access and flexibility.
- VPS Hosting: This hosting option lies in between shared and dedicated hosting. Here, you don’t get full access to the server. You share it with other websites but get the dedicated portion of the resources.

Caching the browser:
Caching is a widely accepted practice to improve your site’s speed. It allows you to store the copies of files on your website.
They try to lessen the work done by the server when a request is made by the browser for some content.
It will lower down your time to first byte (TTFB) by allowing the server to use less resources while a page gets loaded.
When a request is made for the first time, resources need to be extracted from the server.
But when a request is made the second time, these resources will already be there on the browser. This is known as the Browser Caching.
That is why it takes longer for a search result to get loaded the first time as compared to the second time.
You can use W3 Total Cache for caching your website.
It is a caching plugin that can drastically boost up the speed of your WordPress website.
Once it is fully configured, it can 10x improve the speed.
It is compatible with all hosting types and on all devices.
W3 Total Cache helps in giving advance site speed metrics to improve user experience.
It can also be paired with a CDN which will help the users load a site faster.
Use CDN (Content Delivery Network):
To put it simply, it means downloading resources from the nearest of the servers. Your files are not just stored on one single server but a full network of servers.
For example: when a user comes from Germany, they will download the files from their nearest server.
This helps in fetching data from the nearest location, therefore, cutting down on extra time.
This leads to decreased number of requests made while your page gets loaded and the bandwidth is reduced by almost 60%.
You can use Cloudflare for putting your website on CDN.
Cloudflare is a global network of data centers that cache content for users closest to them.
It routes over 10 trillion requests per month via Argo Smart Routing that helps in delivering web traffic over the fastest links available helping in improved user experience.
Page Speed Test
After diagnosing these speed problems, you can go for some tools to ease your task.
A very simple way is to run the Site Speed test in Google Analytics.
Go to: Behavior > site speed
You can also use Site Speed Suggestions to optimize your page in a very customized way:
Go to: Behavior > site speed > speed suggestions
Another good option is to use the Google’s Page Speed Insights tool to give a site speed score. The maximum can go up till 100.
Any score above 80 is decent.
The tool will also give a list of categorized suggestions as low, medium, high, experimental and already done priorities.
You can also use the Webmasters tool for it.
Go to its Lab section and then Site Performance. It will show the speed of your website as experienced by the users.
If you’d like to try yet another option, use a tool such as GTmetrix.
Previous
<< Robots.txt
Next

